#Module 5: Environment Health-I
Spotter 1
1. Write the name of this diagram. (0.5)
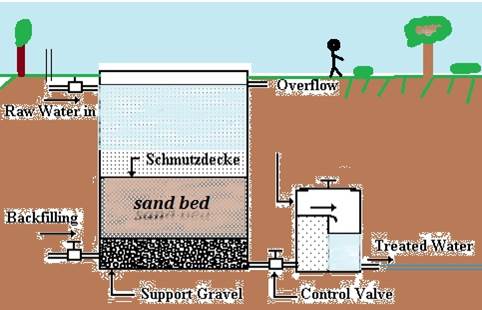
Slow Sand Filter
2. Write two advantages and one disadvantage of the above method. (1.5)
Advantages:
Simple to construct and operate
Cheaper construction cost
Produces high-quality water (physical, biological, and bacteriological)
Disadvantage:
Requires a large area to set up; considered an old-fashioned/outdated method
Spotter 2
1. Enlist 4 points to differentiate Slow Sand Filter (SSF) and Rapid Sand Filter (RSF). (1.5)
Feature | Slow Sand Filter (SSF) | Rapid Sand Filter (RSF) |
|---|---|---|
Filtration rate | Low (~0.1–0.3 m/h) | High (~5–15 m/h) |
Mechanism | Physical, biological & bacteriological purification | Mainly physical filtration; chemical coagulants often needed |
Maintenance | Requires scraping of top layer occasionally | Frequent backwashing needed |
Area required | Large area required | Smaller area required |
Cost | Cheaper to construct | Relatively higher cost |
2. What is the heart of slow sand filter? (0.5)
Sand bed – vital layer responsible for biological and physical purification
Spotter 3
1. Enlist the methods of small-scale water purification. (1)
Boiling
Chlorination (chlorine tablets)
Chemical disinfection (iodine tablets)
Filtration
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation
Reverse osmosis (RO) / multi-stage purification
2. Enlist the methods of large-scale water purification. (1)
Sedimentation / Coagulation-Flocculation
Filtration – slow sand filter or rapid sand filter
Disinfection – chlorination, ozonation, or UV treatment
Softening (if required)
Fluoridation (optional)
Spotter 4
1. Identify the specimen. (0.5)
Chlorination
2. Write the phases of chlorination. (1)
Adding chlorine to water – initial addition of chlorine
Break point chlorination – point at which chlorine demand is satisfied and free chlorine begins to appear
Superchlorination – addition of chlorine beyond the breakpoint to ensure disinfection
Orthotolidine test – used to detect residual chlorine in water
3. How is chlorine demand estimated? (0.5)
Chlorine demand is the difference between the amount of chlorine added to water and the residual chlorine remaining at the end of a specified contact period, under a given temperature and pH.
Spotter 5
1. Identify the specimen. (0.5)
Chlorination
2. How many grams of bleaching powder is required to disinfect 1500 liters of water, where the 4th cup is the 1st cup to show color change? (1.5)
2 grams of bleaching powder are required.
Explanation:
The orthotolidine test determines the first cup to show color change, which indicates the amount of chlorine needed to satisfy chlorine demand and achieve safe disinfection.
Based on the test, for 1500 liters of water, 2 g of bleaching powder is sufficient.
Spotter 6
1. Identify the figure. (0.5)
Modern Sewage Treatment Plant
2. Write the components of primary treatment of sewage. (1)
Screening – removal of large debris
Grit chamber – settling of sand and grit
Primary sedimentation – settling of suspended solids
Skimming / Scum removal – removal of floating materials
3. What is dry weather flow? (0.5)
Dry weather flow is the flow of sewage in sewers during dry weather conditions (i.e., without rain or stormwater).
Spotter 7
1. Identify the figure. (0.5)
Activated Sludge Process
2. Write the components of primary and secondary treatment of sewage. (1)
Primary Treatment:
Screening
Grit chamber
Primary sedimentation
Skimming / Scum removal
Secondary Treatment:
Activated sludge process
Biofilters / Trickling filters
Rotating biological contactors
Secondary clarifiers
3. What is zoogleal layer? (0.5)
Zoogleal layer is a biological slime layer of microorganisms that develops on the surface of a slow sand filter during water purification. It is also called Schmutzdecke and is crucial for biological purification.
Spotter 8
1. Name of the instrument: (0.5)
Stevenson Screen / Thermometer Screen
2. Uses: (1.5)
Acts as a storehouse for thermometers, hygrometers, and barometers
White color reflects heat; slatted sides and double roof ensure air circulation and reduce solar heat absorption
Provides a standard environment for accurate measurement of temperature, humidity, dew point, and atmospheric pressure
3. What is zoogleal layer? (0.5)
Zoogleal layer is a biological slime layer of microorganisms that develops on the surface of a slow sand filter during water purification. It is also called Schmutzdecke and is crucial for biological purification.
Spotter 9
1. Name of the instrument: (0.5)
Kata Thermometer
2. Uses: (1.5)
Ventilation & HVAC: assess air circulation
Industrial Safety (Mining): evaluate airflow in mines
Meteorology: measure low wind speeds and air currents, complementing anemometers
Occupational Health: gauge thermal comfort and heat stress in workplaces
Radiant Heat: estimate radiant heat effects
Spotter 10
1. Name of the instrument: (0.5)
Globe Thermometer
2. Uses: (1.5)
Heat Stress Assessment: indicates heat risk in outdoor work, sports, and military operations
Thermal Comfort: measures combined effect of radiation and convection on people
Building Design: evaluates solar heat gain and loss
Environmental Monitoring: measures Mean Radiant Temperature (MRT) to understand thermal environments, from urban heat islands to industrial settings
Spotter 11
1. Name of the instrument: (0.5)
Anemometer
2. Uses: (1.5)
Meteorology & Climatology: used in weather stations for predicting storms, understanding climate patterns, and tracking atmospheric conditions
Aviation: pilots use it for safe takeoffs, landings, and flight planning
Renewable Energy: measures wind resources to optimize wind turbine placement and operation
Aerospace: used in wind tunnels to test vehicle aerodynamics (cars, planes, spacecraft) for better design
Spotter 12
1. Which type of ventilation is shown in the picture? (0.5)
Mechanical Ventilation
2. List types of ventilation. (1)
Natural ventilation
Mechanical ventilation
Mixed / Hybrid ventilation
3. Mention any two effects of inadequate ventilation. (0.5)
Accumulation of airborne pathogens
Accumulation of carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Spotter 13
1. Mention at least two daylight factors in these areas: (1)
Living Room:
Adequate daylight factor for general activities
Proper distribution of sunlight to avoid glare
Kitchen:
Sufficient direct sunlight for cooking and cleaning tasks
Even illumination to reduce shadows on work surfaces
2. Mention the biological effects of daylight. (1)
Vitamin D synthesis in the skin
Reduces eye strain
Boosts mood and reduces stress
Helps in natural disinfection of living spaces
Spotter 14
1. Write the name of the given spotter. (0.5)
Siphon Flush Toilet
2. Mention the importance of this item. (1.5)
Efficient removal of waste with minimal water usage
Maintains hygiene and odor-free environment due to water seal
Simple and reliable for household use
Spotter 15
1. Write the name of the given instrument. (0.5)
Incinerator
2. What is the ideal temperature for processing by this method? (0.5)
800–1200 °C
3. Enlist 2 drawbacks of this method. (1)
Requires high energy/fuel
Produces air pollutants if not properly controlled
Costly equipment and maintenance
Spotter 16
1. Write the name of the given instrument. (0.5)
Incinerator
2. What is the ideal temperature for processing by this method? (0.5)
800–1200 °C
3. Enlist 2 uses of it. (1)
Medical waste disposal – used bandages, syringes, anatomical waste
Municipal solid waste management
Hazardous or chemical waste disposal
Spotter 17
1. List 3R’s of Health Care Waste Management. (0.5)
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
2. What is the amount of estimated health care waste generated in Nepal (kg/person/day)? (0.5)
1 to 1.7 kg/bed/day
3. Mention latest and best technique of waste management for new hospital settings. (1)
Autoclaving
Spotter 18
1. Enlist the type of waste that is stored in this bin/bag as per latest guidelines for segregation of bio-medical waste. (1)
Infected waste: contaminated dressings, bandages, swabs
Pathological and anatomical waste: body parts, tissues, organs
2. What is the full form of 3R’s in healthcare waste management? (1)
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Note:
Bin/Bag Colour | Type of Waste Stored | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Green | Non‑risk waste (biodegradable) | Food leftovers, garden waste, fruit peels, flowers, etc. (WASH in Health Care Facilities) |
Blue / Dark Blue | Non‑risk waste (non‑biodegradable / recyclable) | Plastic bottles, metals, glass, papers, etc. (WASH in Health Care Facilities) |
Red | Risk/ infectious and pathological waste | Contaminated dressings/bandages, soiled materials, body parts, organs, sharps after disinfection (context varies) (WASH in Health Care Facilities) |
White (Translucent) | Sharps waste (puncture‑proof) | Needles, scalpels, broken glass, blades, etc. (WASH in Health Care Facilities) |
Spotter 19
1. Mention methods for management of Health Care Waste according to guidelines of Nepal 2071. (1)
Waste minimization – reduce the amount of waste generated
Waste segregation – separate waste at the point of generation by type and hazard
Waste collection and storage – use appropriate bins and store safely
Waste transportation – move waste safely to treatment or disposal areas
Waste treatment and disposal – disinfect, recycle, or safely dispose according to type
2. Enlist the type of waste that goes in red bin. (1)
Contaminated but sharpless recyclable wastes: IV tubes & sets, catheters, gloves, syringes, contaminated plastics
Spotter 20
1. Identify this picture. (0.5)
Incinerator
2. Mention the type of wastes that are treated by this instrument. (1.5)
Human anatomical waste
Animal waste
Soiled waste
Expired/discarded medicines
Sharps
3. Write treatment method of infected waste. (0.5)
Autoclaving, incineration, chemical disinfection, or burial
Spotter 21
1. Identify this picture. (0.5)
Inertization
2. Which type of waste is treated by this instrument? (1)
Chemical wastes: acids, alkalis, and toxic chemicals
Pharmaceutical waste: hazardous but non-infectious
Radioactive or heavy metals
Sharps after disinfection
3. Comment on the mixing of this type of waste with others before treatment. (1)
Typical inertization mixture:
65% pharmaceutical waste
15% lime
15% cement
5% water
This mixture stabilizes and neutralizes the waste before safe disposal

