Spotter 1

Identify the condition & draw the epidemiological triad of the given condition. (1)
Condition: Rubella (German Measles)
Epidemiological triad:
Agent factor : RNA paramyxovirus (Rubella virus)
Host factor : young age, immunosuppressed, unvaccinated individuals
Environmental factor : periodic trend – cyclical distribution as well as seasonal distribution (peak during winter & early spring), crowding/schools
Outline its clinical features. (1)
Flu like symptoms
Pink rash (exanthema) on the face which spreads to trunk and limbs
Lymphadenopathy, joint pains, headache & conjunctivitis
Spotter 2
Identify the condition & draw the epidemiological triad of the given condition. (1)
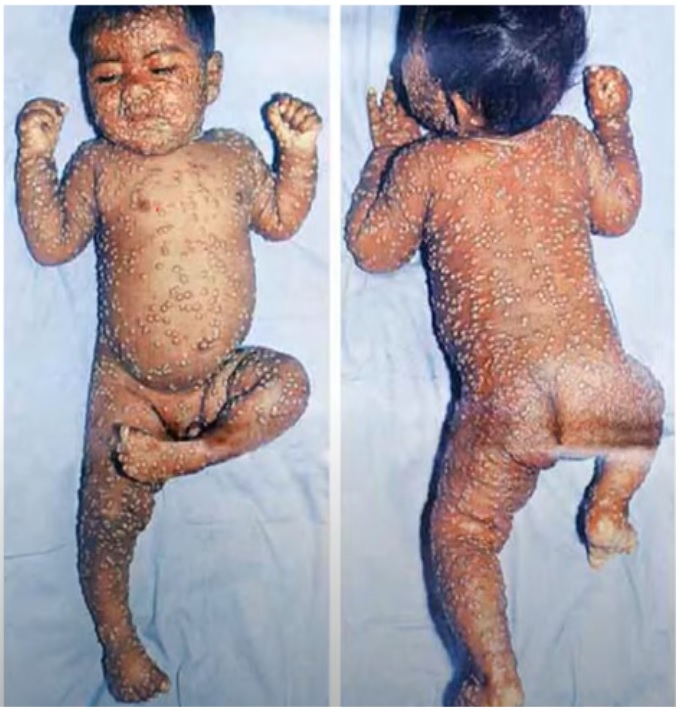
Identified condition: Smallpox
Epidemiological triad:
Agent: Smallpox virus (Variola virus)
Host: young age, non-immune, malnutrition
Environmental factors: overcrowding, cool & dry climates, poor hygiene
Outline its clinical features. (1)
Flu like symptoms
Rash appears first on face, hand, and trunks then to trunk and legs
Starts as macules– papules– vesicles– pustules— scabs
Crusting and recovery
Spotter 3
#1. Identify the condition & draw the epidemiological triad of the given condition. (1)
Diagnosis: Varicella (Chickenpox)
#Epidemiological triad
Agent: Varicella-Zoster virus (Herpes virus)
Host: young age (5–9 years), non-immune
Environmental: overcrowded, cool & dry climate
#2. Outline its clinical features. (1)
Flu like symptoms
Rashes begins on face and trunk spreading to extremities with severe itching
Lesions appear in crops: macules– papules– vesicles– pustules– crusts
Recovers over 7–10 days
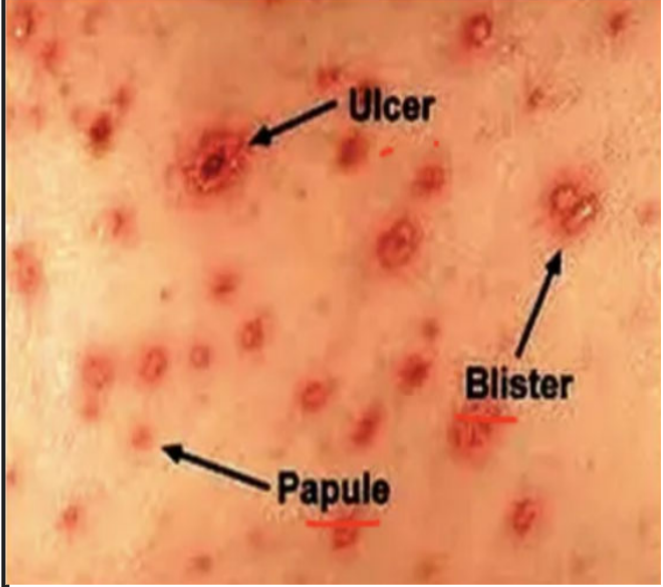
Note: The picture shows typical skin lesions of Varicella (Chickenpox).
Explanation of the picture:
Multiple lesions are present at different stages at the same time (pleomorphism), which is characteristic of chickenpox.
Papule: small, raised red lesion
Blister (vesicle): clear, fluid-filled lesion often described as a “dew drop on a rose petal”
Ulcer/crusted lesion: ruptured vesicle progressing toward healing
Lesions usually appear in crops, mainly over the trunk and face, and are associated with severe itching.
This combination of simultaneous stages of rash helps differentiate varicella from smallpox, where lesions are usually in the same stage.


